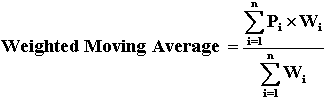In the previous article, we’ve learned Simple Moving Average. In this article, we’ll learn Weighted Moving Average.
Introduction to Weighted Moving Average
As already mentioned, one of the disadvantages of the conventional moving average is the assignment, when calculating it, to all prices of the same weights when averaging, regardless of whether they are closer or further from the current moment. This disadvantage is eliminated in the weighted moving average (Weighted Moving Average). The weighted moving average, therefore, is the usual modification of a simple moving average with weights matched so that the latest prices have an average greater weight.
Formula of Weighted Moving Average:
where Pi are the values of the price of the i-periods back, (i today = 1)
Wi of the weights for the price of the i-periods back
Weights can be chosen in different ways, for example, in the case of a linearly weighted moving average:
Wi = | in-1 | – the weight of the moving average is…