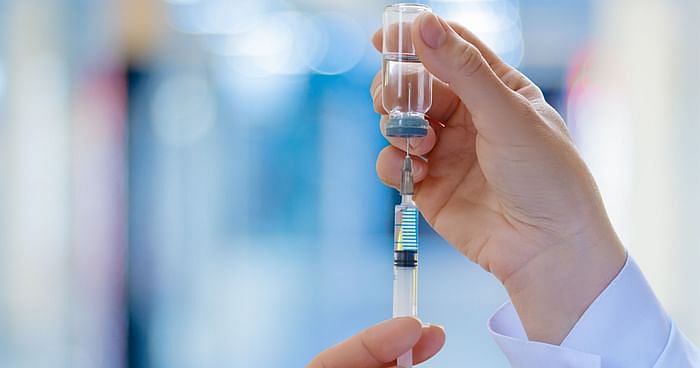
However, they act to prevent or break up fresh blood clots in the blood vessels of the body or the heart itself. They can be best thought of as drugs slowing down or stopping the formation of blood clots.
The drugs usually grouped under this term are of two types – anti-platelet drugs and anticoagulants. The former act against blood cells called platelets which can clump together to initiate the formation of a thrombus or clot. Anticoagulants are drugs which interfere with the action of proteins called coagulation factors that are involved in a cascade of reactions that end in a fibrin clot. Either way, the blood supply to vital organs can get cut off by the clots under conditions of disease, through these pathways are usually meant to be protective. In normal health. If they function inadequately, we would bleed excessively from cuts. If they are overactive, we will have clotting inside arteries, veins or in the chambers of the heart
Examples of anti-platelet drugs are aspirin,…